When building Flutter apps, performance is crucial—especially for CPU-heavy operations like image processing, file parsing, or long loops. Dart uses Isolates to run such operations in parallel so your Flutter UI stays smooth and responsive.
In this article, you’ll learn how to use Isolates in Dart, how it compares with the built-in compute() function, and when to choose which.
What Are Isolates in Dart?
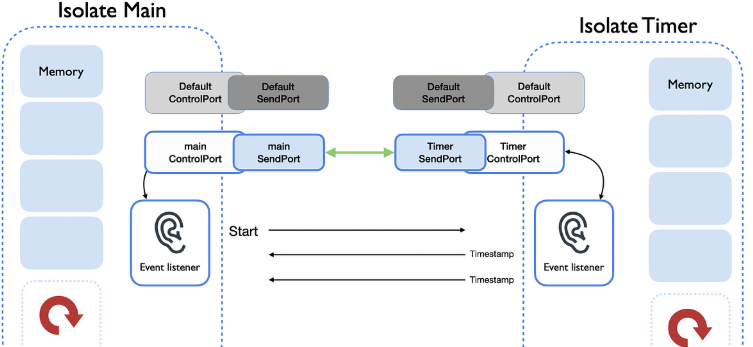
Dart’s Isolate is a way to run code in a separate memory and execution context. Unlike traditional threads, Isolates do not share memory. Communication between Isolates is done using message passing via SendPort and ReceivePort.
Use Case: Running a Heavy Calculation in the Background
Let’s say you need to compute a large mathematical result or parse a big JSON file. Doing this on the main thread causes frame drops and app freezing. The solution: run it in an Isolate.
import 'dart:isolate';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void heavyComputation(SendPort sendPort) {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) {
result += i;
}
sendPort.send(result);
}
class IsolateExamplePage extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_IsolateExamplePageState createState() => _IsolateExamplePageState();
}
class _IsolateExamplePageState extends State<IsolateExamplePage> {
String _result = 'No result yet';
Future<void> _runIsolateTask() async {
final receivePort = ReceivePort();
await Isolate.spawn(heavyComputation, receivePort.sendPort);
final result = await receivePort.first;
setState(() {
_result = 'Computation result: $result';
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Dart Isolate Example')),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Text(_result),
SizedBox(height: 20),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _runIsolateTask,
child: Text('Run Heavy Task in Isolate'),
),
],
),
),
);
}
}
Isolate vs compute() – What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Isolate | compute() |
|---|---|---|
| Use Case | Full control over isolate behavior | Simple one-time background task |
| Memory Management | Manual communication (SendPort) | Automatic serialization |
| Multiple Arguments | Not directly supported | Only one argument allowed |
| Lifecycle Handling | Manual | Automatically managed |
| Complexity | Higher (boilerplate code needed) | Lower (easy to use) |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
An Isolate is Dart’s way to run code in a separate thread and memory space. It helps in handling background tasks without blocking the UI.
Use it for long-running, CPU-bound tasks like data parsing, number crunching, or real-time processing.
compute() is a simplified wrapper over Isolate. It’s easier to use but limited to a single argument and return value.
Not directly. You can combine all values into a single Map or object and pass that.
No. Use Isolate if you need more control or bi-directional messaging. Use compute() for simpler one-shot tasks.
Dart Isolates are powerful tools for improving Flutter app performance when handling heavy operations. For simpler tasks, compute() works well. Choose based on complexity, control, and performance needs.
For more real-world Flutter performance tips, keep reading FlutterFever.com.